How defibrillator device work to control the functioning of the heart?
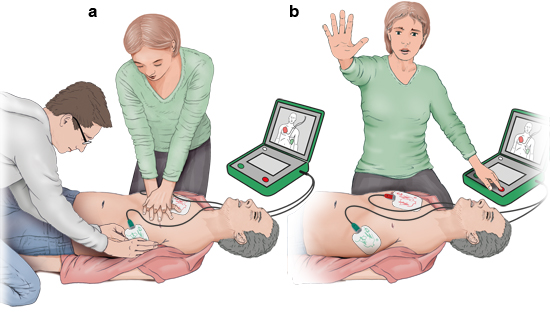
Defibrillators are medical devices that are used in various medical conditions to help with the functioning of the heart and other parts of the body. They are used primarily in emergencies and surgeries to help with quick relief. When used correctly they can be effective and very useful. The main purpose of a defibrillator is to restore the blood flow to the heart through a procedure known as cardio-vascular resuscitation (CVR).
It is very common for emergency situations to have a cardiac
arrest or stroke, where a person may go into cardiac arrest and have a heart
attack or stroke. The most common problem that is faced in these cases is when
the patient's heart has stopped beating due to a malfunction. This can happen
in many different ways, for example, it could be due to cardiac arrhythmia or
due to other structural problems. There are many patients that cannot be
resuscitated in these situations. A defibrillator provides a powerful dose of
electrical current to the injured or dying heart to bring it back to a normal
heartbeat. If this happens, the person would likely pass away from the injury
and will not survive for very long.
How defibrillators
work is that they use a device called a probe that is inserted into the chest.
This probe is attached to a receiver which is linked to an electronic circuit
board. The circuit board sends the electrical impulses to a heart pacemaker,
which in turn activates the muscles of the heart to pump blood. As the cardiac
muscles contract, the blood flow to the heart is increased and the circulation
is normal. In a situation such as this, defibrillators can provide significant
relief to the person that has cardiac arrhythmia or has had a stroke.
Defibrillators are also useful for those that are suffering from
cardiac disease and need to be monitored while they are at home or in their
office.


Comments
Post a Comment